QC Visualization
1. Read-Level QC (Visualization)
The qc_visualization() function performs read-level
quality control visualization based on precomputed read count tables. It
serves as the R-side visualization companion to the bash-based QC step
(qc.sh), transforming pairwise read counts into a
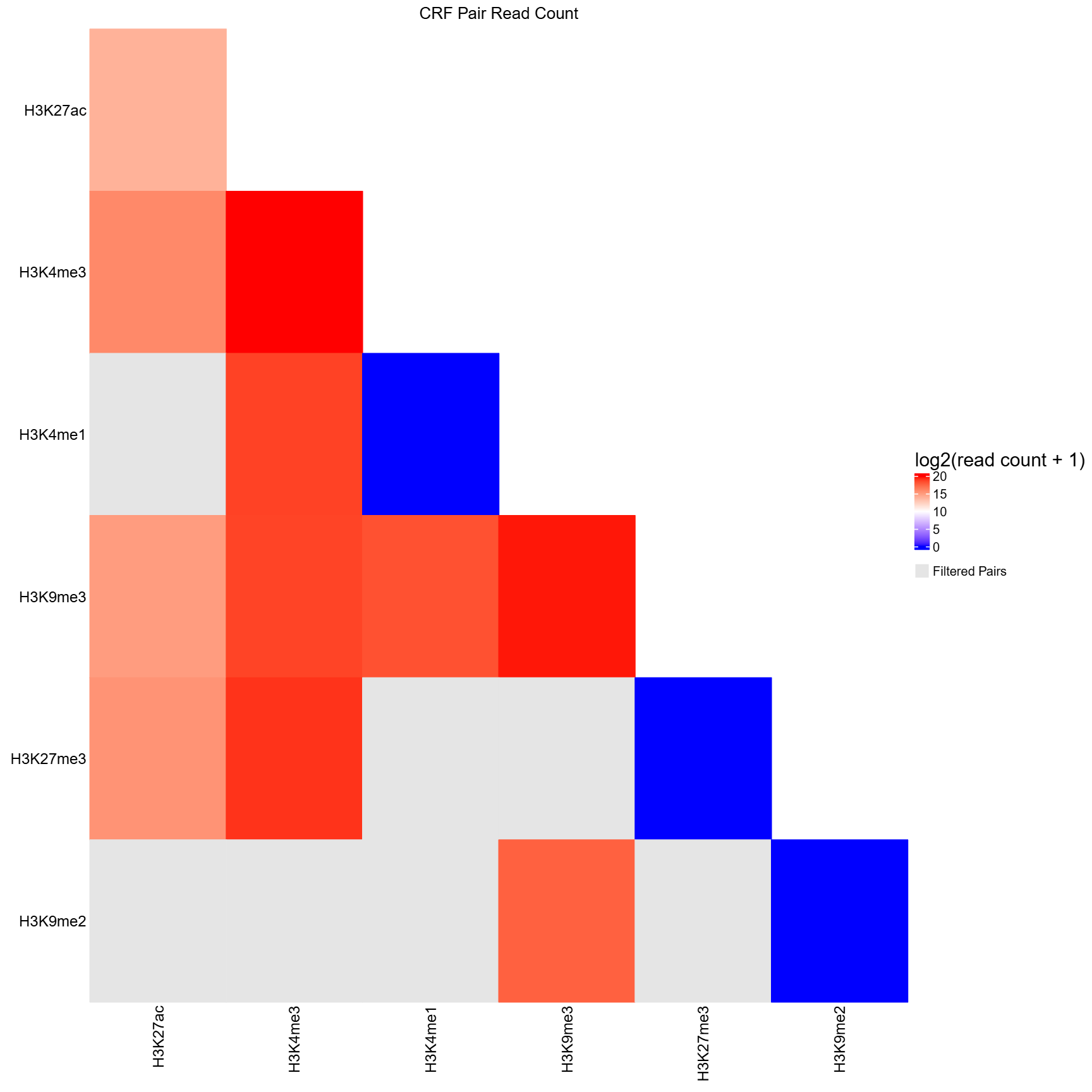
CRF-by-CRF heatmap for diagnostic inspection.
What this function does:
Unlike earlier integrated QC command, qc_visualization()
does not compute read counts or apply filtering itself.
Instead, it consumes two TSV files generated upstream.
- Reads
all_read_count.tsvandfiltered_read_count.tsv, both containing CRF pair names (pair) and corresponding read counts (read_count). - Converts the pairwise table into a symmetric CRF-by-CRF matrix, filling only the lower triangle.
- Marks CRF pairs that fail QC (i.e., not present in the filtered
table) as
NA, which are displayed in grey in the heatmap. - Applies a log2(read count + 1) transformation to stabilize dynamic range.
- Generates a publication-quality PDF heatmap summarizing sequencing depth across all CRF pairs.
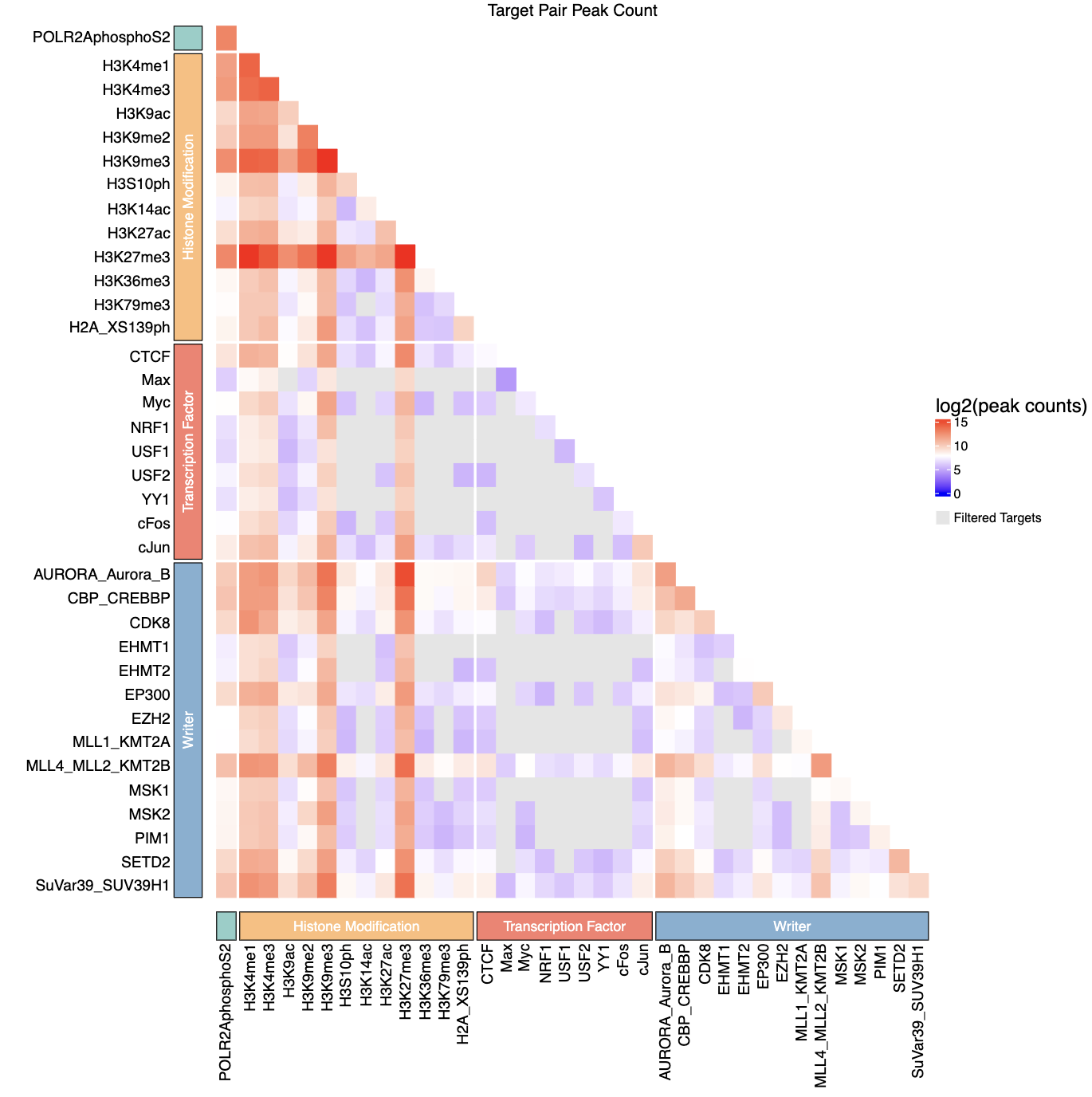
- Optionally annotates CRFs by biological categories (e.g., histone marks, TFs) using a user-provided grouping CSV.
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
all_read_count_path
|
character | — |
Path to all_read_count.tsv containing all CRF pairs and
their read counts
|
“qc/all_read_count.tsv”
|
filtered_read_count_path
|
character | — |
Path to filtered_read_count.tsv containing CRF pairs that
pass QC
|
“qc/filtered_read_count.tsv”
|
out_dir
|
character |
“.”
|
Output directory for the heatmap PDF |
out_dir = “./qc”
|
split_pair_by
|
character |
“-”
|
Delimiter used to split CRF pair names into individual CRFs |
split_pair_by = “_“
|
group_csv
|
character |
NULL
|
Optional CSV defining CRF groupings for heatmap annotation |
“crf_groups.csv”
|
crf_col
|
character |
“crf”
|
Column name in group_csv specifying CRF identifiers
|
crf_col = “CRF”
|
category_col
|
character |
“category”
|
Column name in group_csv specifying CRF categories
|
category_col = “group”
|
Output Files
The function generates the following output files in the specified
out_dir:
- Peak count heatmap -
qc_heatmap.pdf(ifplot= TRUE)- PDF visualization of log2-transformed read counts for CRF-CRF pairs
- Lower triangle matrix showing read counts between CRF pairs
- Filtered (non-significant) pairs displayed in grey
- If
group_csvprovided, includes categorical annotations with colored blocks
Example Usage
library(multiEpiCore)
# ===== General Usage =======
# Define QC directory
qc_dir <- "qc"
# Optional: Create grouping CSV
crfs <- c("H3K4me1", "H3K4me3", "H3K9ac", "H3K9me2", "H3K9me3", "H3K27ac", "H3K27me3", "H3K36me3")
categories <- c(rep("Active", 3), rep("Repressive", 3), rep("Other", 2))
group_df <- data.frame(crf = crfs, category = categories)
write.csv(group_df, file.path(qc_dir, "crf_groups.csv"), row.names = FALSE)
# Run QC with grouping
qc_visualization(
all_read_count_path = file.path(qc_dir, "all_read_count.tsv"),
filtered_read_count_path = file.path(qc_dir, "filtered_read_count.tsv"),
out_dir = qc_dir,
split_pair_by = "-",
group_csv = file.path(qc_dir, "crf_groups.csv")
)
# ===== Test Data =======
bam_dirs <- list(
"C1" = 'qc/C1',
"C2" = 'qc/C2',
"T1" = 'qc/T1',
"T2" = 'qc/T2'
)
for (name in names(bam_dirs)) {
qc_by_percentile(
all_read_count_path = file.path(bam_dirs[[name]], "all_read_count.tsv"),
filtered_read_count_path = file.path(bam_dirs[[name]], "filtered_read_count.tsv")
)
}2. (Optional) Fragment Length Analysis
The frag_decomposition() function analyzes fragment
length distributions from BAM or BED files to characterize chromatin
structure patterns.
What this function does:
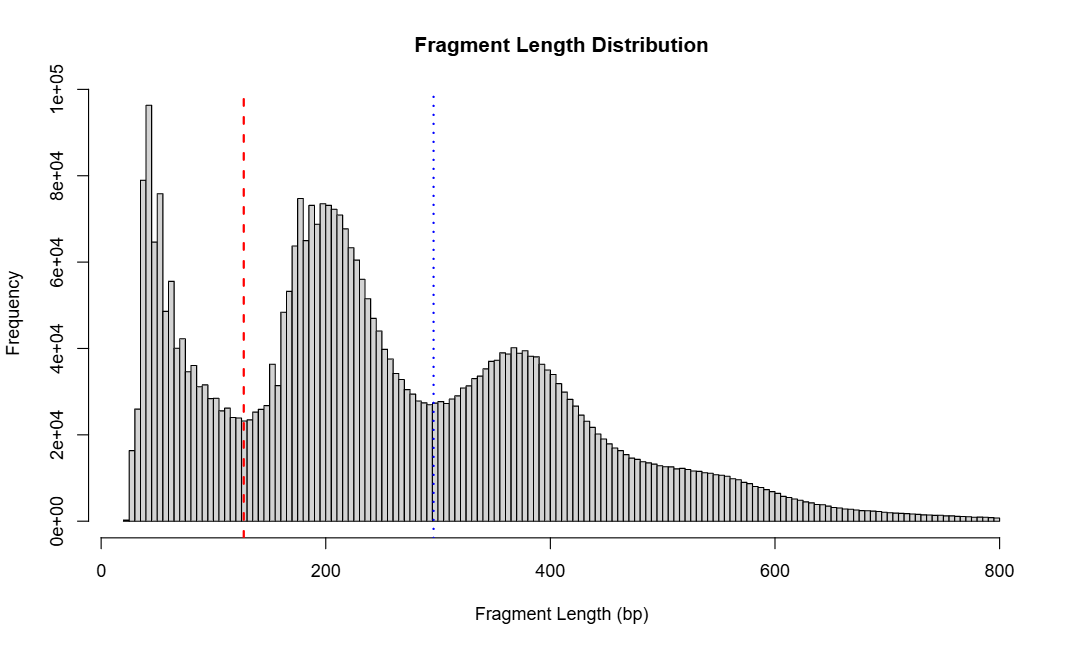
This function reads sequencing data files and extracts fragment lengths for all samples. It generates a combined histogram showing the overall fragment length distribution across all samples.
When detect_valley = TRUE, the function uses kernel
density estimation to identify two valley positions in the distribution:
the first valley (~150 bp) separates nucleosome-free regions from
mononucleosome-bound fragments, and the second valley (~300 bp)
separates mononucleosomes from dinucleosomes. These valleys serve as
thresholds to classify each fragment into one of three categories:
subnucleo (short fragments from open chromatin), monomer (single
nucleosome), or dimer+ (multiple nucleosomes).
The function then calculates the count and percentage of fragments in each category for every sample, providing a quantitative assessment of chromatin accessibility. All results are saved as a histogram PDF and a TSV file containing per-sample decomposition statistics.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
file_path
|
character vector | — | Vector of BAM or BED file paths to analyze for fragment length distribution |
file_path = c(“sample1.bam”, “sample2.bam”)
|
out_dir
|
character |
“.”
|
Output directory |
out_dir = “./frag_analysis”
|
detect_valley
|
logical |
FALSE
|
If TRUE, detects valley positions in the fragment length distribution to classify fragments into subnucleo, monomer, and dimer+ categories |
detect_valley = TRUE
|
dens_reso
|
numeric |
2^15
|
Resolution for kernel density estimation; higher values produce smoother curves |
dens_reso = 2^16
|
dens_kernel
|
character |
“gaussian”
|
Kernel type for density estimation (options: “gaussian”, “epanechnikov”, “rectangular”, “triangular”, “biweight”, “cosine”) |
dens_kernel = “epanechnikov”
|
valley1_range
|
numeric vector |
c(73, 221)
|
Range to search for the first valley (NFR/mononucleosome boundary) |
valley1_range = c(100, 180)
|
valley2_range
|
numeric vector |
c(221, 368)
|
Range to search for the second valley (mono/dinucleosome boundary) |
valley2_range = c(250, 350)
|
Output Files
The function generates the following output files in the specified
out_dir:
- Fragment length histogram -
fragment_distribution.pdf- Shows the combined fragment length distribution across all samples
- If
detect_valley = TRUE, includes red and blue vertical lines marking the two detected valley positions - Visualizes the overall chromatin structure pattern
- Fragment decomposition data -
fragment_decomposition.tsv(only ifdetect_valley = TRUE)- Per-sample statistics table with the following columns:
pair: Sample name (filename without extension)total_count: Total number of fragmentssubnucleo_count/subnucleo_pct: Count and percentage of fragments < valley1 (nucleosome-free regions)monomer_count/monomer_pct: Count and percentage of fragments between valley1 and valley2 (mononucleosomes)dimer_plus_count/dimer_plus_pct: Count and percentage of fragments ≥ valley2 (dinucleosomes and higher)
- Per-sample statistics table with the following columns:
| pair | total_count | subnucleo_count | subnucleo_pct |
|---|---|---|---|
| H3K27ac-H3K27ac | 15198 | 6052 | 39.8210290827741 |
| H3K27ac-H3K27me3 | 43569 | 9697 | 22.2566503706764 |
| H3K27ac-H3K4me1 | 31754 | 6028 | 18.9834351577754 |
| H3K27ac-H3K4me3 | 60573 | 11751 | 19.3997325541083 |
| H3K27ac-H3K9me3 | 32173 | 7423 | 23.0721412364405 |
| H3K27me3-H3K4me3 | 574643 | 127471 | 22.1826420925688 |
| H3K4me1-H3K4me3 | 432292 | 86923 | 20.1074736520685 |
| H3K4me1-H3K9me3 | 307657 | 65218 | 21.1982825029172 |
| H3K4me3-H3K4me3 | 940240 | 191717 | 20.3902195184208 |
| H3K4me3-H3K9me3 | 415540 | 98901 | 23.8005968137845 |
| H3K9me2-H3K9me3 | 201788 | 49676 | 24.6179158324578 |
| H3K9me3-H3K9me3 | 820666 | 178360 | 21.7335676145959 |
| pair | monomer_count | monomer_pct | dimer_plus_count | dimer_plus_pct |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3K27ac-H3K27ac | 4766 | 31.3593893933412 | 4380 | 28.8195815238847 |
| H3K27ac-H3K27me3 | 20374 | 46.762606440359 | 13498 | 30.9807431889646 |
| H3K27ac-H3K4me1 | 12538 | 39.4847893178812 | 13188 | 41.5317755243434 |
| H3K27ac-H3K4me3 | 21792 | 35.9764251399138 | 27030 | 44.6238423059779 |
| H3K27ac-H3K9me3 | 13164 | 40.9162962732726 | 11586 | 36.0115624902869 |
| H3K27me3-H3K4me3 | 274641 | 47.7933255951956 | 172531 | 30.0240323122356 |
| H3K4me1-H3K4me3 | 176829 | 40.9049901455498 | 168540 | 38.9875362023817 |
| H3K4me1-H3K9me3 | 134247 | 43.6352821486266 | 108192 | 35.1664353484562 |
| H3K4me3-H3K4me3 | 343196 | 36.500893388922 | 405327 | 43.1088870926572 |
| H3K4me3-H3K9me3 | 178033 | 42.843769552871 | 138606 | 33.3556336333446 |
| H3K9me2-H3K9me3 | 79756 | 39.5246496322873 | 72356 | 35.8574345352548 |
| H3K9me3-H3K9me3 | 341684 | 41.634964772514 | 300622 | 36.63146761289 |
Example Usage
library(multiEpiCore)
# ===== Test Data =======
bam_dirs <- list(
"C1" = 'bam/C1',
"C2" = 'bam/C2',
"T1" = 'bam/T1',
"T2" = 'bam/T2'
)
for (name in names(bam_dirs)) {
bam_dir <- bam_dirs[[name]]
bam_paths <- list.files(path = bam_dir, pattern = "\\.bam$", recursive = TRUE, full.names = TRUE)
frag_decomposition(
file_paths = bam_paths,
out_dir = file.path("qc", name),
detect_valley = TRUE
)
}